Neutrophil
Inflammation Assays
- Respiratory Burst (ROS, Phagoburst)
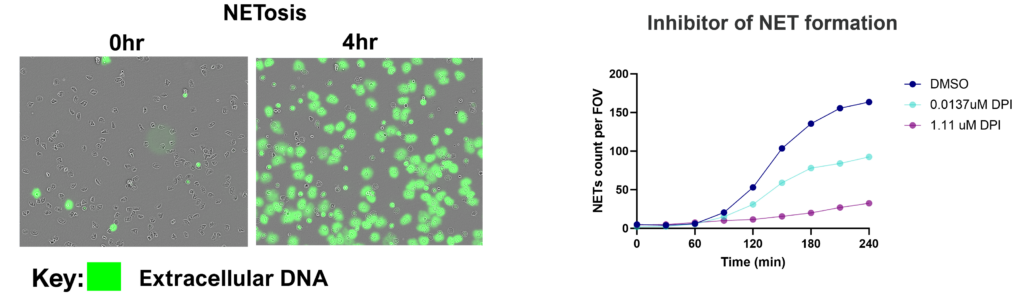
- NETs
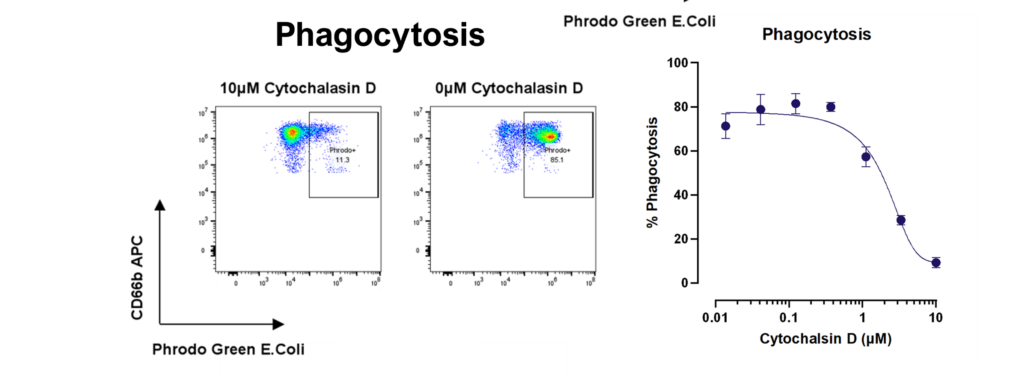
- Phagocytosis/trogocytosis
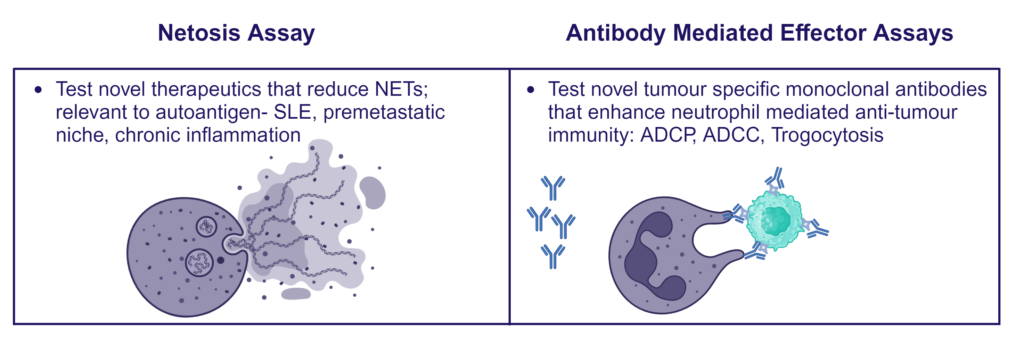
Therapeutic blocking of NETosis and enhancement of neutrophil phagocytosis/trogocytosis
Neutrophils are armed with a variety of effector mechanisms, they release neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs), comprising of chromatin and antimicrobial proteins which are released via a unique, pro-inflammatory form of cell death called NETosis. Dysregulated NET release can damage the host, contributing to autoimmune diseases such as Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) by the release of autoantigens. Similarly, dysregulated NET release contributes to diseases such as atherosclerosis, deep vein thrombosis and has been shown to promote cancer progression and metastasis. Modulating neutrophil function is therefore a potential therapeutic intervention.

Drug Discovery Tool
Find the right immune assay for your therapeutic area, modality and target using this interactive Drug Discovery Tool.
